Middle East Space Roundup: 3 to 9 February 2025
A summary of all the space news in the Greater Middle East over the past week, brought to you by AzurX
The following are the major space developments in the Greater Middle East region tracked by Middle East Space Monitor over the past week:
UAE Space Developments
UAE’s MBRSC Taps Thales Alenia Space for Gateway Airlock Amidst Artemis Program Uncertainty
In a significant development for lunar exploration infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space has secured a contract from the UAE's Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) to construct the airlock module for NASA's lunar Gateway station, marking the final major component of this ambitious orbital facility. The module, designed to enable astronaut spacewalks, scientific payload deployment, and additional vehicle docking capabilities, is scheduled for launch on the Artemis 6 mission no earlier than 2030. This agreement, stemming from the UAE's January 2024 deal with NASA that exchanges the airlock's contribution for a future Artemis mission seat, further cements Thales Alenia Space's prominent role in Gateway's development, as the company is already involved in producing several other crucial components including the HALO module structure, Lunar I-Hab, and ESPRIT module. However, the project faces uncertainty amid potential policy shifts, with questions surrounding the Gateway's necessity for lunar operations and the possibility of program revisions under new administration directives, despite NASA officials maintaining the station's strategic importance for long-term lunar exploration and Mars mission preparation.
UAE’s MBRSC Gateway Airlock Secures Emirati Astronaut Artemis Seat
The UAE has taken a significant step in its space ambitions by partnering with Thales Alenia Space to develop a critical airlock module for NASA’s Lunar Gateway station, reinforcing its role in international space exploration. Announced by Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed, the agreement between the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) and the Italian-French aerospace firm marks a strategic expansion of the UAE’s participation in NASA’s lunar orbiting station, expected to be operational by 2030. The airlock will serve as the entry and exit point for astronauts and cargo, a crucial component for future missions. In return for its contribution, the UAE is set to secure a seat for an Emirati astronaut on a future Gateway mission, advancing its goal of deep space human exploration. This move aligns with the UAE’s broader space strategy, following the success of its astronaut corps, which includes Hazza Al Mansouri, Sultan Al Neyadi, Nora Al Matrooshi, and Mohammed Al Mulla, all trained for future missions. With NASA, Japan, and European and Canadian space agencies collaborating on the Gateway, the UAE’s involvement reinforces its commitment to becoming a key global player in space exploration and lunar missions.

UAE’s Hope Mars Probe Completes Four Years Orbiting Mars
The UAE’s Hope probe has completed four years in orbit around Mars, continuing to provide valuable scientific data that enhances global understanding of the Red Planet’s atmosphere, climate history, and potential for past life. Since entering orbit on 9 February 2021, Hope has contributed critical insights into Martian weather, seasonal changes, and auroras, while also enabling researchers to study biosignature gases like methane that could indicate microbial activity. The probe’s ultraviolet spectrometer has revealed an extensive Martian aurora, offering new perspectives on how solar winds interact with the planet’s atmosphere, which may help explain Mars' atmospheric loss. The mission’s success has bolstered the UAE’s position in space exploration, paving the way for the ambitious MBR Explorer mission, set to launch in 2028. This spacecraft will conduct flybys of Venus and Mars before exploring seven asteroids, testing advanced thermal management and electric propulsion technologies. The UAE Space Agency is leveraging local industry partnerships to ensure long-term sustainability and knowledge transfer from the Mars mission to the private sector. As the UAE expands its space ambitions, the Hope probe's legacy continues to shape its growing influence in planetary exploration and technological innovation.
UAE Utilizes Earth Observation Satellites to Protect Nuclear Power Plant from Climate Change Threats
The UAE is integrating satellite monitoring technology to safeguard its Barakah nuclear power plant from climate change threats, marking a regional first in nuclear infrastructure resilience. Since September 2024, the Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) and the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) have been tracking environmental risks from space, including rising sea levels, extreme temperatures, and seismic activity. With the Middle East’s increasing exposure to extreme weather events, the initiative underscores the growing reliance on space-based climate monitoring for energy security. FANR aims to provide early warning of potential threats to ensure the plant’s long-term operational stability, crucial for maintaining 60 years of uninterrupted energy production. While few global energy operators have adopted satellite surveillance for infrastructure resilience, this UAE-led initiative positions the country at the forefront of climate-adaptive nuclear energy management.
UAE Companies ALIENSENSE and Madari Space Partner on Space-Based data Centers
In a major step toward advancing space-based data processing and storage, UAE companies ALIENSENSE and Madari Space have announced a strategic partnership to integrate advanced visual sensing and autonomous data management technologies into orbital data centers. Under this collaboration, ALIENSENSE will develop space-grade visual systems to enhance Madari Space's satellite-based infrastructure, enabling debris avoidance, cataloging, visual positioning, and technical data collection. Positioned in low-Earth orbit (LEO), Madari Space’s data centers aim to provide sustainable, energy-efficient storage solutions while reducing reliance on terrestrial data facilities. The project will leverage secure blockchain-based storage and low-latency computing, offering enhanced security and efficiency for industrial applications. The UAE Space Agency has welcomed the initiative as a testament to its Space Economic Zones program, which fosters commercial partnerships and positions the UAE as a leader in space technology innovation. This partnership represents a significant step toward the future of space-centric data processing, aligning with the UAE’s vision for a knowledge-driven space economy.
UAE’s MBRIF Selects Satellite IoT Company Krucial for 9th Cohort Innovation Accelerator
Krucial, a Scotland-based satellite Internet of Things (IoT) company, has been selected for the 9th Cohort of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Innovation Fund (MBRIF) Innovation Accelerator in the UAE, marking a strategic step in its expansion into the region. The program supports high-potential companies in advancing technologies across critical sectors, including space, energy, infrastructure, and food security. CEO and co-founder Allan Cannon highlighted the alignment of the initiative with Krucial’s mission to digitize industrial operations globally. Krucial's participation is further backed by AzurX, a key investor specializing in space and strategic technologies, which has facilitated its entry into the UAE market. With access to expert mentors and a network of partners, Krucial aims to accelerate its growth and enhance its impact in the region’s innovation ecosystem.
Israel Space News

Israel Opens First Dedicated Solar Observatory on Mount Carmel
Israel has launched its first dedicated solar observatory, Solaris, in the Druze village of Usfiya, marking a significant step in its space and solar research capabilities. Operated by Space Valley and funded by the Israel Space Agency for its initial three years, the observatory is designed as both a scientific hub and an educational resource for the public. Equipped with four advanced apochromatic telescopes and specialized cameras, Solaris will enable in-depth studies of the Sun’s different layers and wavelengths, enhancing understanding of solar radiation and its effects on Earth. The facility also includes a 12-inch telescope for deep-sky observations and a Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope for planetary imaging, positioning it as a leading center for astronomy research. Beyond academic contributions, Solaris will explore solar radiation’s impact on climate change, human health, aviation, and agriculture, while also advancing research into solar energy applications. Its location in Usfiya reflects Israel’s commitment to regional inclusivity and scientific outreach, with planned workshops and educational programs to inspire future generations in space and solar science. Innovation, Science, and Technology Minister Gila Gamliel emphasized Solaris as a symbol of Israel’s leadership in space innovation, while Israel Space Agency Director-General Uri Oron hailed it as a national asset that strengthens the country’s position in solar research and aerospace technology.
Israel’s OdySight.ai Seeks $21.5 Million in NASDAQ IPO Listing
Israel’s Odysight.ai is poised to become the first Israeli Nasdaq IPO of 2025, seeking to raise $21.5 million at a $129 million valuation. The company, currently traded over-the-counter with a market cap of $111 million, has transformed from its medical device origins into a provider of AI-powered visual monitoring solutions for critical infrastructure and machinery, securing prestigious clients including NASA, the Israeli Air Force, and Safran. Under the leadership of CEO Yehu Ofer, former Sde Dov air base commander and Elbit Systems executive, the company has demonstrated significant growth with revenues reaching $2.66 million in the first three quarters of 2024 (up 145% year-over-year) and an order backlog expanding from $2.6 million to $15 million throughout 2024, though it continues to operate at a loss having consumed $42 million to date. The upcoming IPO, led by The Benchmark Company, will see controlling shareholder Mori Arkin's 51.1% stake reduce to 44.6%, with other major stakeholders including Phoenix Finance, Meitav, and Mor maintaining significant positions in this emerging player in the industrial monitoring sector.
New Study Finds Women Persistently Underrepresented in Israel’s Space Sector
A recent report by SpaceIL and The Parasol Foundation highlights the persistent gender gap in Israel’s space industry, where women comprise less than a quarter of the workforce and hold fewer than 10% of engineering roles. Leadership representation is even lower, with only two female CEOs among Israel’s 49 space start-ups and minimal presence in management positions. While the number of women pursuing space-related studies has grown by 54% over five years, disparities in high school STEM participation remain a key barrier. The report stresses the need for systemic change, including stronger early STEM education initiatives, mentorship programs, and workplace policies promoting gender diversity. Globally, women’s participation in space remains stagnant at around 20%, reflecting broader industry challenges. SpaceIL and the Parasol Foundation are taking steps to address this imbalance through initiatives like the Beresheet-2 engineering program, research scholarships, and new educational outreach efforts. These measures aim to inspire more women to enter and advance within the space sector, fostering long-term industry growth and inclusivity.
Iran Space Developments
Analyst: Iran’s Human Spaceflight Program Aims for 2029 Astronaut Launch
In Press TV, Ivan Kesic writes that Iran is advancing its human spaceflight program, targeting 2029 for its first astronaut launch, positioning itself as the fourth country to independently send humans into space. Since achieving independent satellite launch capability in 2008, Iran has steadily progressed, launching numerous communications and Earth observation satellites, developing five types of satellite launch vehicles, and pioneering bioastronautics research. The country became the sixth country to send animals into space and the fifth to launch a mammal, demonstrating its expertise in space biology and life sciences. Iran’s Kavous capsule took its first suborbital flight in December 2023, with plans to develop a 1.5-ton crewed capsule by 2025 and conduct a series of test missions before full crewed operations. The Sarir and Soroush launch vehicles, designed for geostationary and heavy-payload launches, are expected to facilitate human spaceflight, with operational capability by 2027-2028. Despite sanctions and geopolitical challenges, Iran’s self-reliant space strategy continues to expand, reinforcing its position among emerging spacefaring countries.
Opinion: Starlink’s Direct-to-Device Satellite Internet Could Bolster Resistance in Iran
In the Middle East Forum, journalist Babak Taghvaee writes that Iran’s ongoing economic crisis, compounded by sanctions, mismanagement, and foreign military interventions, has exposed the regime’s vulnerabilities, particularly in the face of precision Israeli airstrikes. Nationwide protests, if reignited, could pose a significant threat to the government, but Iran has long relied on internet censorship and blackouts to suppress dissent. While Virtual Private Networks (VPN) and proxy servers have provided limited access to the outside world, complete internet shutdowns have rendered them ineffective, as seen during the 2019 and 2022 protests. In response, Iranian human rights organizations facilitated the delivery of Starlink terminals, but high costs and government GPS jamming have limited their widespread adoption. SpaceX’s ongoing development of direct-to-cell satellite internet, successfully tested in early 2024, presents a potential game-changer. By enabling Iranians to bypass censorship using their existing mobile devices, this technology could provide secure access to independent news, social media, and communication platforms. If expanded in Iran, it could significantly undermine state-controlled narratives, empower protest organizers, and challenge the regime’s ability to isolate its population during future uprisings. Rather than investing in easily bypassed circumvention tools, Western governments should prioritize supporting direct-to-cell connectivity as a means of facilitating free information flow and grassroots resistance efforts.
Azerbaijan Space News
Azerbaijan’s Azercosmos Taps Qala Insurance to Insure Azerspace-1 Satellite
Azerbaijan’s state space corporation Azercosmos has awarded Qala Insurance OJSC a $810,000 contract to provide orbital insurance for the Azerspace-1 telecommunications satellite in 2025, valued at $53 million. This marks a shift from PASHA Insurance OJSC, which previously insured Azerspace-1 when it was valued at $66.5 million in 2024 and $80 million in 2023. The declining valuation reflects aging satellite infrastructure or shifting market assessments. The contract was secured through an open tender, reinforcing Azerbaijan’s strategic focus on cost-efficient risk management in its growing satellite sector, which plays a critical role in the country’s telecommunications and digital development initiatives.

Azerbaijan Students to Build and Launch PicoSatellite in 2025
Azerbaijan is set to achieve a milestone in space education with its first-ever student-built satellite launch aboard a SpaceX rocket in 2025. Organized under the Azerbaijan National Satellite Innovation Competition, this initiative reflects the country's growing commitment to STEM education, digital literacy, and space research. The PocketQube picosatellite, measuring 5x5x5 cm and weighing 250g, will be developed by schoolchildren in grades 7-9 as part of a collaboration involving the KOSMIK Academy, Azercosmos, the Innovation and Digital Development Agency, and international partners like the Brazilian Space Agency and IDEIA Space. The project aligns with Azerbaijan’s strategy to foster a new generation of engineers and scientists, integrating students into the global space ecosystem through hands-on experience in satellite design, programming, and research. Leveraging SpaceX’s Rideshare program, the initiative makes satellite deployment more economically viable, further accelerating Azerbaijan’s technological development and international recognition in space innovation. By engaging young minds in space exploration, Azerbaijan is positioning itself as a regional leader in space education and commercial satellite technologies.
Azerbaijan’s Azercosmos Reports Slight Dip in 2024 Export Revenues for SATCOM Services
Azerbaijan’s state space corporation, Azercosmos, exported $18.5 million in satellite telecommunications services to 50 countries in 2024, marking a slight decline of 6.57% from the previous year. According to the January "Export Review" by the Center for Analysis of Economic Reforms and Communication, service exports accounted for 73% of Azercosmos' total revenue, with December 2024 alone contributing $1.6 million from 40 countries. The United Kingdom led as the top market with $6 million in service exports, followed by Luxembourg ($3.8 million), the UAE ($855,500), Pakistan ($683,800), and Türkiye ($654,500). Despite the minor decline, Azercosmos continues to play a significant role in global satellite telecommunications, reinforcing Azerbaijan’s position in the space economy.
Türkiye Space Developments
Türkiye On Track to Launch Its First Lunar Mission, AYAP-1, In 2026
Türkiye is advancing its lunar ambitions with two planned Moon missions under the National Space Program, with the first, AYAP-1, set for a 2026 launch. The mission will utilize a domestically developed hybrid rocket engine and aims to achieve a hard landing on the Moon, marking a significant milestone for Türkiye’s space sector. The Turkish Space Agency (TUA), alongside TÜBİTAK Space Technologies Research Institute and Delta V, is leveraging its expertise from satellite projects to propel the Lunar Research Program forward. The second mission, AYAP-2, will feature a soft landing using domestically produced propulsion technology, with additional plans for a rover mission. Türkiye is also investing in the development of fusion-based propulsion systems using Bor-11, a naturally occurring element in the country. Currently, mission risks have been assessed, preliminary and mission designs completed, and the critical design phase is in progress. Additionally, discussions are ongoing for key services such as ground station leasing and launch operations. By accelerating its efforts in space and aviation technologies, Türkiye is positioning itself among the leading countries in lunar exploration and propulsion research.

The Economist: Türkiye’s Space Program Advances But Faces Challenges
Türkiye’s space ambitions, closely tied to its defense industry, are advancing despite financial and talent retention challenges, according to The Economist. The Turkish Space Agency, founded in 2018, has seen increasing state investment, rising from $4.7 million in 2013 to $140 million in 2025, with major projects such as homemade satellites, a Moon mission, and a $350 million spaceport in Somalia. The spaceport serves both civilian and military purposes, including the planned testing of Türkiye’s new 2,000 km-range missile, marking a significant step in the country’s defense expansion. Baykar’s sister company, Fergani Space, is spearheading Türkiye’s push into satellite-based military applications, aiming to launch 100 satellites within five years to establish a Turkish global navigation satellite system (GNSS). This aligns with Türkiye’s broader defense goals, where satellites, including Türksat-5B, are already integrated with drones for global operations. President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s administration is also strengthening ties with China and Russia, applying to join the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), positioning itself as an alternative to Western space initiatives such as Artemis. However, economic pressures and a growing brain drain among Turkish engineers may challenge the sustainability of these ambitions, as talent continues to seek better salaries abroad despite state-driven investments in the defense and aerospace sectors.

Experts From Türkiye to Assist Malaysia on Satellite Launches From Sarawak
Sarawak, a state in Malaysia, is exploring the feasibility of launching satellites using aircraft or floating vessels as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional rocket launches. Sarawak Premier Datuk Patinggi Tan Sri Abang Johari Tun Openg has tasked i-CATS University College, led by chairman Tan Sri Datuk Amar Abdul Aziz Husain, to collaborate with international experts, including those from Türkiye, to develop the necessary expertise for this initiative. Speaking at the Sarawak Multimedia Authority’s (SMA) Lunar New Year Dinner 2025, Abang Johari highlighted that these advanced launch methods could significantly reduce environmental impact while positioning Sarawak as a player in the global space industry. This initiative aligns with broader regional ambitions to enhance technological capabilities and leverage innovative solutions for satellite deployment. The move signals Sarawak’s intent to integrate space technology into its development strategy, fostering international partnerships and expertise to establish a niche in the evolving satellite launch sector.
Bahrain Space News
Bahrain’s King Restructures Board of Directors of National Space Science Agency
In a strategic move to advance Bahrain’s space science ambitions, King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa issued Order (5) of 2025, restructuring the Board of Directors of the National Space Science Agency (NSSA). The newly appointed board, chaired by Sheikh Khalid bin Ali bin Jaber Al Khalifa, includes key figures from academia, economic development, and government sectors, such as the President of the University of Bahrain, the Chief Executive of the Labour Fund (Tamkeen), and other industry leaders. The four-year term aims to provide continuity and strong leadership in shaping Bahrain’s space initiatives. The restructuring signals Bahrain’s commitment to strengthening its role in the regional and global space sector by fostering innovation, collaboration, and investment in satellite technology, space research, and economic development.
Bahrain’s NSSA Participates in COPUOS Workshop on Space Sustainability
Bahrain’s National Space Science Agency (NSSA) participated in the inaugural Sustainable Space Days event in Vienna, Austria, organized by the United Nations and the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), highlighting the country’s commitment to space sustainability. NSSA’s delegation of experts, engineers, and legal professionals engaged in discussions on mitigating risks posed by space debris and managing orbital congestion. The event featured simulations of spacecraft collisions, workshops on space situational awareness, and strategies for coordinated space traffic management. NSSA CEO Dr. Mohammed Ibrahim Al-Asiri emphasized the urgency of addressing space sustainability challenges amid increasing satellite launches and corporate competition in space services. He warned of the growing risk posed by space debris traveling at high velocities, which could endanger spacecraft and astronauts. NSSA's engagement in this global initiative underscores Bahrain’s strategic role in promoting responsible space activities and advocating for sustainable solutions in the rapidly evolving space economy.
Saudi Arabia Space Developments
Neo Space Group COO Calls for Risk-Sharing Strategies in Small Satellite Market
The 2025 SmallSat Symposium opened with a session on Risks, Realities, and Regulations, highlighting the 30% CAGR growth of the SmallSat market while emphasizing Saudi Arabia's increasing role in satellite investments. Robert Cleave, COO of Neo Space Group, underscored Saudi Arabia’s commitment to risk-sharing strategies to ensure the success of its growing space sector. Speaking from his base in the Kingdom, Cleave noted that Saudi Arabia is actively investing in SmallSat technology and fostering strategic partnerships to strengthen its position in the global space economy. He emphasized that while the SmallSat industry presents lucrative opportunities, market players must remain adaptable to changing parameters, evolving business models, and regulatory uncertainties.
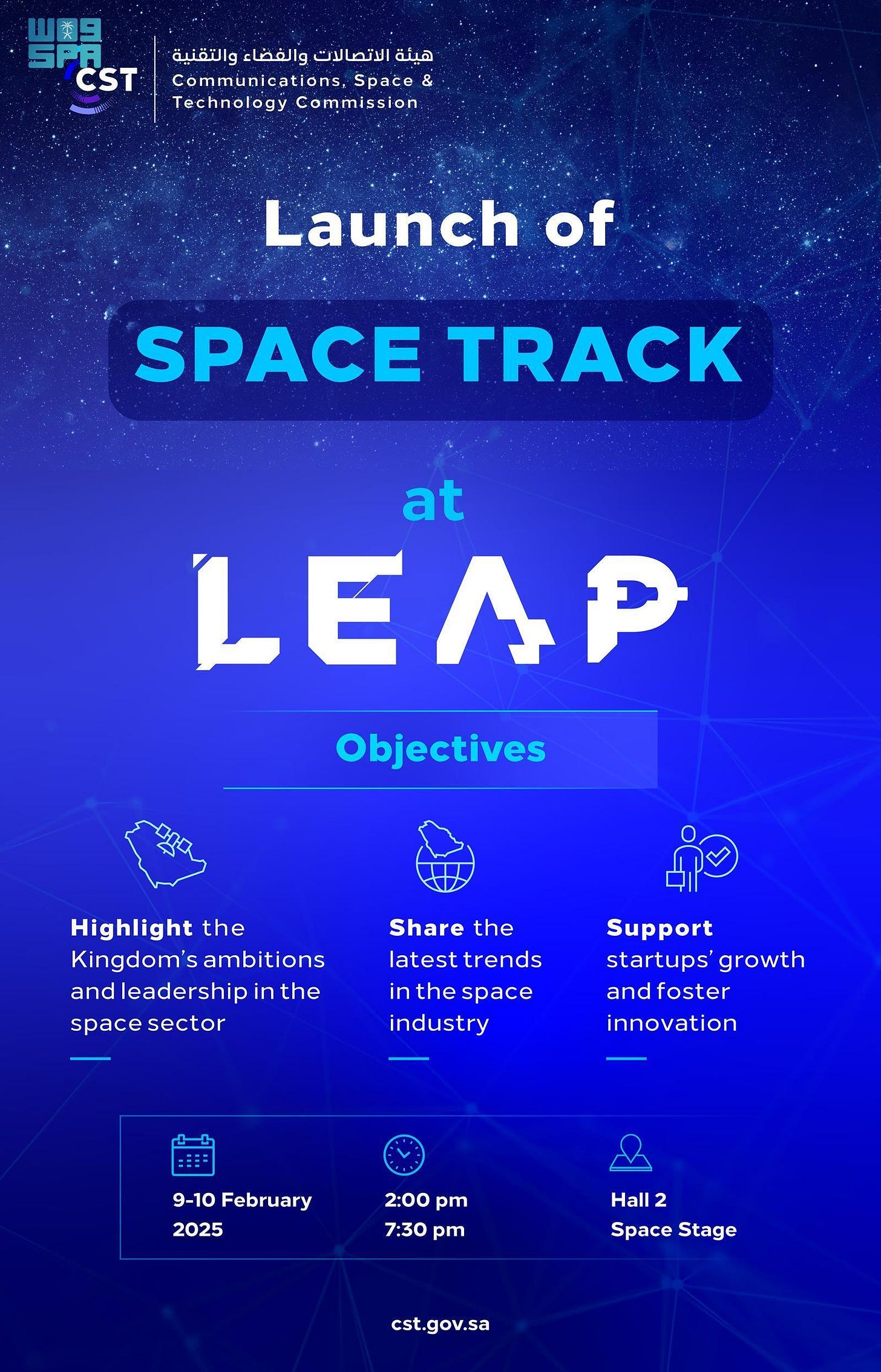
Saudi Arabia’s LEAP 25 Features Space Track to Showcase Space Advancements
As part of the LEAP 25 global technology conference, Saudi Arabia’s Communications, Space & Technology Commission (CST) is launching the second edition of the Space Track, a dedicated platform aimed at showcasing advancements in the space sector and fostering innovation. Held from 9 to 10 February 2025, in Hall 2, the event will feature expert discussions on emerging trends, technological developments, and Saudi Arabia’s strategic ambitions in space. The initiative is designed to position the Kingdom as a regional leader in space technology by connecting startups with investors, industry experts, and global partners. By leveraging this platform, CST aims to accelerate the growth of Saudi Arabia’s space ecosystem, drive investment in emerging space enterprises, and inspire the next generation of innovators to contribute to the industry’s expansion.
AIRMO Expands into Gulf Region with Funding and Recognition for Methane Monitoring Tech
AIRMO, a Berlin-based methane monitoring space and climate tech company, is steadily expanding into the Gulf region and gaining recognition. The startup received $40K in funding and was awarded $100K from KAUST Innovation at the TAQADAM Cohort 8 Startup Accelerator Showcase 2025 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. AIRMO is developing a 12-satellite constellation equipped with an in-house designed methane detection instrument—a combination of micro-LiDAR, SWIR spectrometer, and RGB camera sensors—deployable on both drones and satellites. The company's first satellite, funded by ESA, is set for launch next year. AIRMO has also recently established a presence in Abu Dhabi, UAE, joining the Climate Tech program at HUB71.
![SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket carrying Telefix's satellite "Bluebone" is launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on the 14th of last month. [Picture = Telefix] SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket carrying Telefix's satellite "Bluebone" is launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on the 14th of last month. [Picture = Telefix]](https://substackcdn.com/image/fetch/$s_!mpbE!,w_1456,c_limit,f_auto,q_auto:good,fl_progressive:steep/https%3A%2F%2Fsubstack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fpublic%2Fimages%2F532e592f-b4e7-48f1-8faf-87418822a36d_700x394.jpeg)
Saudi Arabia Expresses Interest in Blue Carbon Satellite Imagery from South Korea’s Telepix
South Korea’s Telepix has successfully launched BlueBON, the world's first dedicated blue carbon monitoring satellite, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base. The satellite, which achieved successful orbital insertion and systems validation, features an advanced multispectral camera and the TetraFlex AI processor, enabling high-resolution monitoring of marine and coastal ecosystem carbon absorption, including floating algae distribution. Of particular note is the satellite's potential impact on the emerging carbon credits market, with Telepix actively pursuing data distribution partnerships, including promising discussions with institutions and companies in Saudi Arabia, highlighting the Kingdom's interest in advanced environmental monitoring capabilities and its potential role in the growing blue carbon market. The company reports that BlueBON will deliver approximately 2,500 times higher resolution analysis compared to existing detection services, marking a significant advancement in maritime environmental monitoring technology.
Egypt Space News

Egypt’s Nilesat and Eutelsat Strengthen Satellite Cooperation for Middle East and Africa
In a strategic effort to enhance regional and international satellite communications, Nilesat chairman and CEO, Major General Sameh Katta, met with Eutelsat CEO, Eva Berneke, in Cairo, Egypt, to discuss expanding collaboration between the two satellite operators. The discussions focused on broadening cooperation in satellite operations, optimizing television broadcasting services, and leveraging advanced technologies to meet evolving consumer demands. Nilesat reaffirmed its commitment to strengthening partnerships with global satellite operators, particularly Eutelsat, which has emerged as a key player in the European and African satellite markets. With the 2023 merger of Eutelsat and OneWeb, creating the first fully integrated GEO-LEO satellite operator, the company now operates 35 geostationary satellites and a constellation of over 600 LEO satellites, supporting video broadcasting, mobile and fixed connectivity, and government services. The two companies explored joint service expansions, aiming to enhance connectivity and broadcasting solutions across the Middle East and Africa, while positioning themselves to address emerging industry challenges and maintain leadership in the satellite communications sector.
Egyptian Space Agency Finishes African Development Satellite Workshop
The Egyptian Space Agency (EgSA) recently hosted a transformative training program under the African Development Satellite Initiative (AfDev-Sat), bringing together 21 engineers and specialists from 20 African countries. The initiative, funded by the Italian government, aimed to strengthen indigenous satellite development capabilities through a nine-day intensive workshop on space technology, including hands-on experience with satellite assembly and mission operations. Participants explored EgSA’s state-of-the-art facilities, such as the Mission Control Center and Ground Earth Station, while gaining insights into hyperspectral imaging, orbital mechanics, and CubeSat development. The program underscored Africa’s growing ambitions in space, with EgSA and the African Space Agency (AfSA) driving regional collaboration to expand access to world-class infrastructure. The engagement of international partners, including the Italian Space Agency, further emphasized the importance of knowledge transfer and resource-sharing in accelerating Africa’s space capabilities. As Africa integrates space technology with telecommunications and embraces LEO constellations, initiatives like AfDev-Sat are key to positioning the continent as a major player in the global space industry. Additionally, the program’s strong representation of women highlighted efforts to close gender disparities and promote diverse participation in STEM fields. By fostering space awareness at the grassroots level and enhancing education pathways, Africa is actively cultivating a skilled workforce ready to contribute to the rapidly evolving space sector.
Other Regional Space Developments
Kuwait Commits to Expanding Its Role in the Global Space Sector
Kuwait reaffirmed its commitment to expanding its role in the global space sector during its participation in the 62nd session of the Scientific and Technical Subcommittee of the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS). This year marked a significant milestone as Dr. Hala Al-Jassar represented the Kuwait National Space Research Center (Kuwait-NSRC) in its inaugural participation following the center’s establishment in September 2024. Kuwait emphasized its longstanding engagement in space, dating back to its 1963 participation in the International Telecommunication Union conference, the launch of the Umm Al-Aish space communications ground station in 1969, and its first satellite, KuwaitSat-1, in 2023. Dr. Al-Jassar underscored Kuwait’s commitment to international space governance, citing its adherence to the 1967 Outer Space Treaty, the UN Moon Agreement, and other regulatory frameworks. She highlighted Kuwait's advancements in satellite-based remote sensing technologies, particularly in environmental and climate monitoring, which have been integral to national research initiatives since the 1980s. Kuwait is now focused on strengthening international partnerships to advance space science, foster innovation, and support sustainable space operations. The COPUOS session in Vienna, running until 14 February 2025, addresses critical topics such as space sustainability, remote sensing, space debris mitigation, and the role of space technology in global health, reinforcing Kuwait’s aspirations for a stronger presence in international space cooperation.
Hong Kong’s USPACE Forms Strategic Partnership With Tunisia-Based AICTO for Regional Satellite Constellation
Hong Kong-based USPACE Technology Group Limited has entered a strategic partnership with the Arab Information and Communication Technologies Organization (AICTO), headquartered in Tunisia, to advance satellite manufacturing and operations across the Middle East and Africa. This collaboration will support USPACE in securing radio frequencies for its planned satellite constellation, strengthening its market position and contributing to regional socio-economic development. USPACE, a subsidiary of Hong Kong Aerospace Technology Group Limited, specializes in satellite manufacturing, telemetry, tracking, and data applications. With advanced cleanroom facilities for satellite assembly and testing, the company aims to establish itself as a leading satellite manufacturer by 2028 and deploy a dedicated constellation for the Middle East and Africa by 2030, reinforcing its ambitions in the rapidly growing space sector.
Oman and Pakistan Deepen Military Space Cooperation
During his visit to Oman, Pakistan’s Air Chief Marshal Zaheer Ahmed Baber Sidhu engaged in high-level discussions aimed at strengthening aerospace and defense collaboration between the two countries. A key focus of the visit was Oman’s interest in Pakistan’s National Aerospace Science & Technology Park, signaling potential avenues for joint technological advancements in aerospace industries. The Omani leadership acknowledged Pakistan’s growing indigenous aerospace capabilities and expressed a strong desire for enhanced collaboration, particularly in space, cyber, and electronic warfare domains. The discussions also emphasized expanding bilateral and multilateral aerial exercises, knowledge-sharing initiatives, and industrial partnerships. Oman’s participation as observers in Exercise Indus Shield-2024 was highlighted, where they commended Pakistan’s integration of niche and disruptive technologies in airpower strategy and space operations. The visit reinforced Pakistan’s commitment to providing tactical and technological support to Oman, paving the way for deeper aerospace cooperation in the region.
Business Executive: LEO SATCOM Unlocks New Business Opportunities in the Middle East
The rapid advancement of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications is unlocking new business opportunities, particularly in the Middle East and Africa (MEA), where the demand for high-speed, resilient connectivity is surging, writes Raed Rached for Forbes. As the Middle East positions itself as a global digital hub, key drivers such as AI-driven initiatives, hyperscaler data centers, and digital government transformation underscore the need for low-latency, scalable networks. Saudi Arabia, for example, has committed $100 billion to AI and tech initiatives under Vision 2030, demonstrating the region’s growing reliance on LEO-based connectivity to support its ambitious smart city and industrial automation projects. The low latency of LEO satellite communications makes them ideal for financial services, AI/cloud computing, oil and gas operations, autonomous systems, and smart cities. Despite the opportunities, regulatory concerns regarding national security, environmental impact, and data governance remain challenges that must be addressed. To maximize LEO’s potential, the MEA region should leverage public-private partnerships for infrastructure expansion, tap into emerging talent in newly connected areas, and foster an entrepreneurial ecosystem to drive local innovation. As technological advancements and regulatory clarity continue to shape the landscape, the MEA region is poised to become a leader in satellite-enabled digital transformation, enhancing connectivity, economic growth, and technological resilience.
Be sure to catch up with space activities in the region in the next edition of Middle East Space Monitor’s space roundup!